The inversions of the augmented triad chord In the tables below the different inversions of a augmented triad are positioned on the guitar fretboard First inversion – interval 1, 3, #5;Third inversion – interval #5, 1, 3;G Diminished Triad 2nd Inversion Db (G) A Diminished Triad Root Position (A) C Eb A Diminished Triad 1st Inversion C Eb (A) B Diminished Triad 2nd Inversion F (B) D Sets found in the same folder Music Theory > Chords > Triads > Augmented 21 terms Adrian_coronado2522 TEACHER Music Theory > Harmonia > Fundamentos 10 terms
Augmented Triads The Nandi Method
G augmented triad second inversion
G augmented triad second inversion-The second inversion of the same triad contains an augmented fourth Only the first inversion contains no augmented nor diminished intervals Because of this, composers prefer first inversion diminished triads While root position diminished triads are used occasionally, second inversion is rarely encounteredB Minor Triad 2nd Inversion F# (B) D Sets found in the same folder Music Theory > Chords > Triads > Diminished 22 terms Adrian_coronado2522 TEACHER Music Theory > Chords > Triads > Augmented 21 terms Adrian_coronado2522 TEACHER Music Theory > Harmonia > Fundamentos 10 terms Adrian_coronado2522 TEACHER Music Theory > Chords > Triads



Unit 13 Music 110 Fundamentals Of Theory
7 C is the third above the bass of the firstinversion major triad whose root is the submediant degree of the harmonic minor scale whose parallel major is the relative major of the minor key that has a signature of three sharps 8 G is the sixth above the bass of the secondinversion minor triad whose triadic fifth is ^6 of the The root position would be GD, the first inversion would be DG, and the second inversion would be DG Diminished and Augmented Triads These triads are used less frequently in modern music in comparison to major and minor triads, but they are important to known nonetheless Building an augmented or diminished triad is more complicated in terms ofUppercase numerals with a small plus sign represent augmented triads Lowercase numerals with a small circle represent diminished triads Let's apply Roman numerals to the C major scale Since the first triad is major, its numeral is uppercase Second inversion is represented with both a small 6 and 4 This is due to the root and third
This step shows the Gflat major 2nd inversion on the piano, treble clef and bass clef The Gflat major 2nd inversion contains 3 notes Db, Gb, These note names are shown below on the treble clef followed by the bass clef The figured bass symbols for this chord inversion are 6/4, so the chord is said to be in sixfour positionMajor triads Minor triads Diminished triads Augmented triads Chords Second Inversion Second inversion triads have the middle note as the root of the chord 2nd Inversion on 654 play notes play chord 2nd Inversion on 543 play notes play chord 2nd Inversion4 Inversion It's second inversion because the fifth is the lowest note Answer E flat major second inversion Writing and Playing Example Question Write (or Play) an F minor triad in first inversion 1 Root It's F the directions said so 2 Quality An a minor triad has a minor third on the bottom and a major third on the top 3
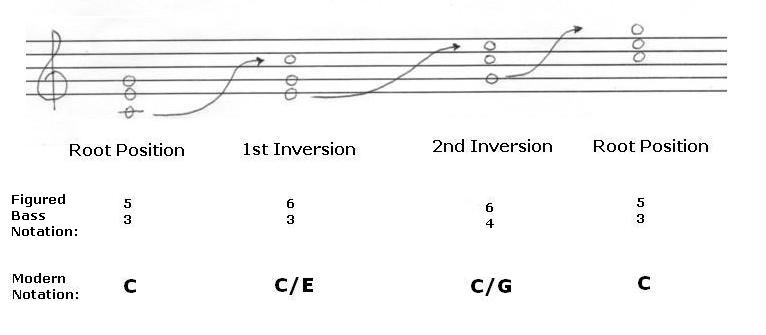
Practice recognising all the inversions of major, minor, diminished, and augmented chords After completing this module you will be able to reliably recognise the four types of triad chord in all their different inversions This module has a sequence of lessons with which you will gradually learn to recognise the three inversions of triad chordsThe figured bass notation for this triad in 2nd inversion is 6/4, with the 6 placed above the 4 on a staff diagram Based on this numbering scheme, another name for this inversion would be A augmented triad in sixfour positionC–E ♭ –G Augmented triad First and secondinversion C major triads, written as C/E and C/G An inverted chord is a chord with a bass note that is a chord tone but not the root of the chord Inverted chords are noted as slash chords with the note after the slash being the bass note




Augmented Triads The Nandi Method




Basicmusictheory Com G Augmented Triad Chord
An augmented triad is a chord, made up of two major thirds (an augmented fifth)The term augmented triad arises from an augmented triad being considered a major chord whose top note (fifth) is raised When using popularmusic symbols, it is indicated by the symbol "" or "aug"For example, the augmented triad built on C, written as C, has pitches C–E–G ♯It's the root note that determines what the chord is G Augmented Chord Charts for Guitar, Free & Printable View our G guitar chord charts and voicings in Standard tuning with our free guitar chords and chord chartsIf you are looking for the G chord in other tunings, be sure to scroll to the bottom of the page For over 950,000 charts and voicings, grab an account



Augmented Triads The Nandi Method




Section 6 2 Basic Chord Concepts Offtonic Theory
However, inversion is not discussed until the chapter Inversion and Figured BassG Shape C Major Triad When in the G shape, the root position chord can be built on the lowest root We can use the fourth from the root on the low E string to find the 3 A fourth from that 3 is 6, and two frets down from that 6 is 5 You can look at the same diagram above to find the 351 or first inversion The second inversion triad can beIn a second inversion C diminished triad what is the bass note E G E flat none from MUT 1004 at University of Central Florida




Basicmusictheory Com G Augmented Triad Chord




Basicmusictheory Com G Augmented Triad Chord
F Major Triad 2nd Inversion C (F) A G Major Triad Root Position (G) B D G Major Triad 1st Inversion B D (G) G Major Triad 2nd Inversion D (G) B A Major Triad Root Position Music Theory > Chords > Triads > Augmented 21 terms Adrian_coronado2522 TEACHER Music Theory > Harmonia > Fundamentos 10 terms Adrian_coronado2522 TEACHER1st inversion 3rd 5th 1st 2nd inversion 5th 1st 3rd Before doing Ear test 12 listen to Audio Demo 2, which helps you to identify the inversions of the major triad Michael row the Boat Ashore begins with a major triad in root position (C E G) In the Mood begins with a major triad in 1st inversion (E G C)Inversion Compare the inversions of the minor triad to the inversions of the augmented triad A minor triad in root position contains a minor third (eg, CE~) and a major third (E~G), which together span a perfect fifth (CG) Its first inversion yields a major third (Ei>G) and a perfect fourth (GC), which together span a major sixth



Augmented Chords For Guitar Theory Formulas Charts Bellandcomusic Com



Unit 13 Music 110 Fundamentals Of Theory
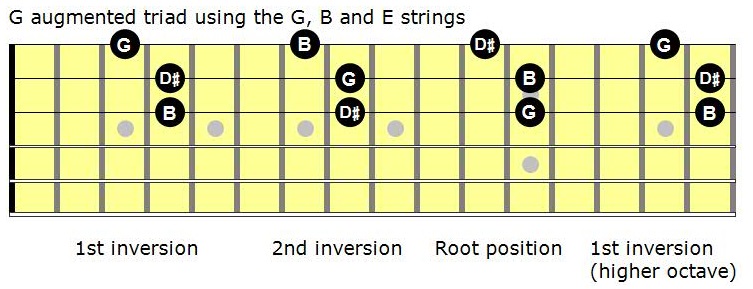
Its inversion is determined by which of these tones is the lowest note (or bass note) in the chord The term inversion often categorically refers to the different possibilities, though it may also be restricted to only those chordsNow, the augmented triad is what's called a symmetrical structure That means that mathematically, its notes are chosen in such a way that each inversion of the chord is exactly the same shape And because each chord is the same as its inversions, each inversion of the chord is also another augmented triad Second Inversion Second Inversion of C Major Seventh Taking this pattern one step further, the second inversion of a seventh chord has the fifth in the bass We know that the above example is a second inversion seventh chord since the fifth (G) is the lowest note Third Inversion Third Inversion of C Major Seventh Finally, we have the third




Major Thirds Tuning Wikipedia




Click Here To A Pdf Of The Lesson
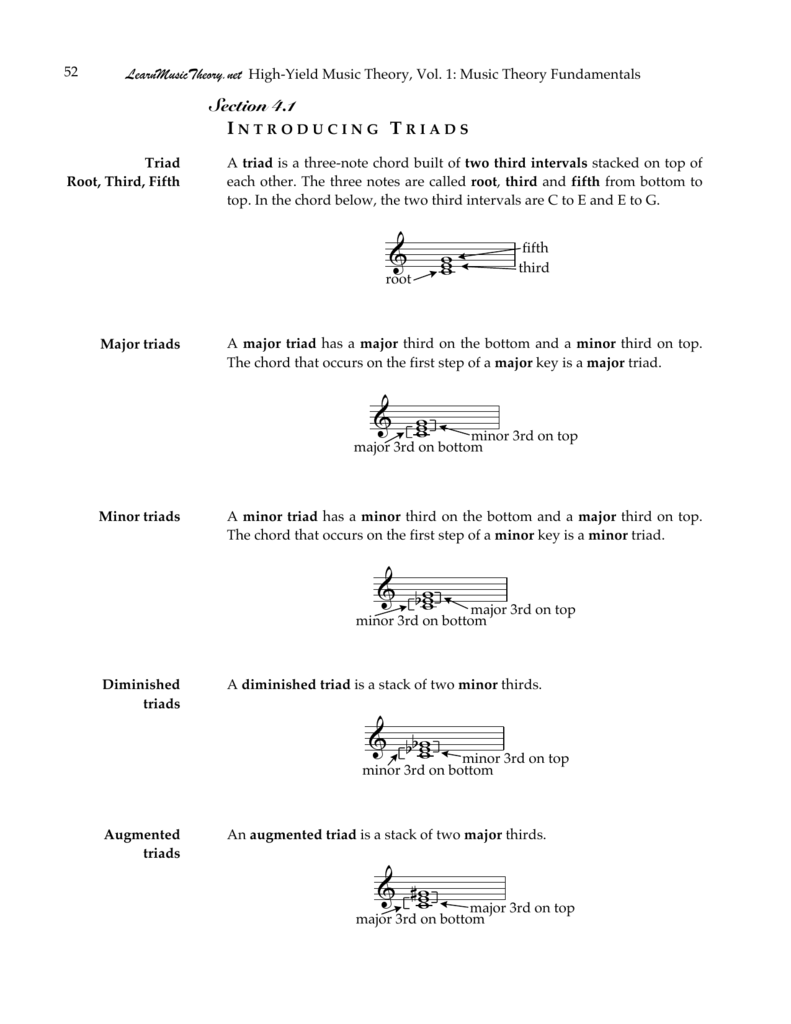
133 Triad qualities As with intervals, triads come in different qualities Triads may be major, minor, diminished, or augmented To determine the quality of a triad, one must consider the qualities of the intervals contained therein The following example shows a major triad and a minor triad built on the same rootThe third string is G radio because sharp 513 That is how you playing an augmented triad second inversion and those who your augmented triads on strings 23 and four 11 Augmented triads quiz in this lesson, I'm going to quiz you on the different augmented triads in the different inversionsG Flat Augmented Triad Second Inversion harga yamaha t max 750 cc harry potter knjige komplet harga mesin cuci sharp 6 5 kg harley davidson chopper for sale near me harley davidson cenik harry potter set knjiga na engleskom harry potter kamen modrosti obnova harry potter set knjiga harvey norman maribor razvijanje fotografij harley davidson




What Is A Chord Max Neil




5 2 Naming Triads
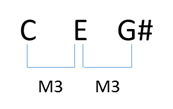
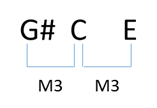
If we then move the 3rd up an octave we have the second inversion – 5th, Root, 3rd – G,C,E OTHER TRIADS It is really simple to find other (minor, augmented, diminished) triads from the major triad Major triad – R,3,5 – C,E,G Minor triad – R,m3,5 – C,Eb,G (Lower the 3rd one 1/2 step) Augmented triad – R, 3, #5 – C,E,G# (Raise the 5th one 1/2 step) Diminished triad –This 24 x 36 oneofakind triads poster is an incredibly powerful tool for guitar players, teachers and songwriters The poster is printed on 100lb glossy stock poster paper Each poster is shipped rolled up in a plastic bag and packaged in a shipping tube • Major Triads • Minor Triads •Is a sixth, while the interval from E to G is a third In first inversion triads, the interval between the root and other chord tones are a sixth and third Consequently, first inversion triads are represented (by music scholars) as chord sixthree and all first inversion triads



2




Augmented Triads The Nandi Method
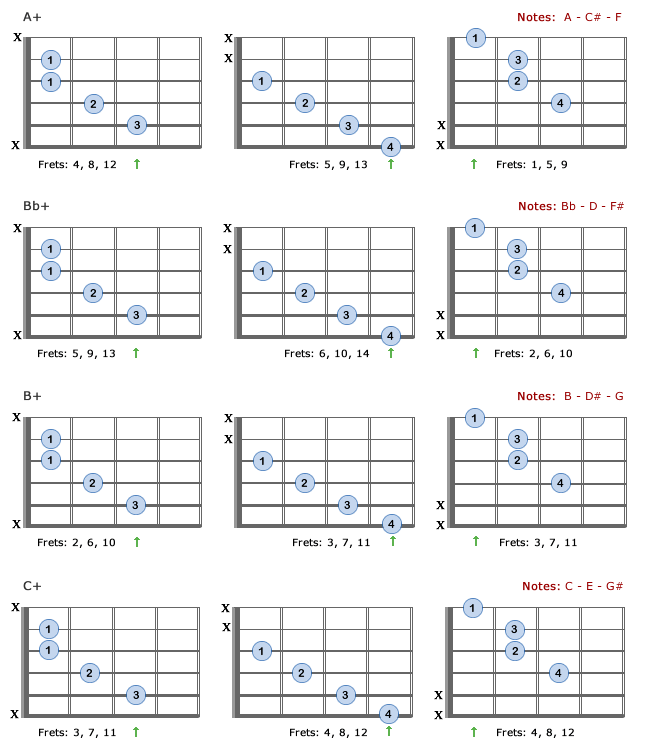
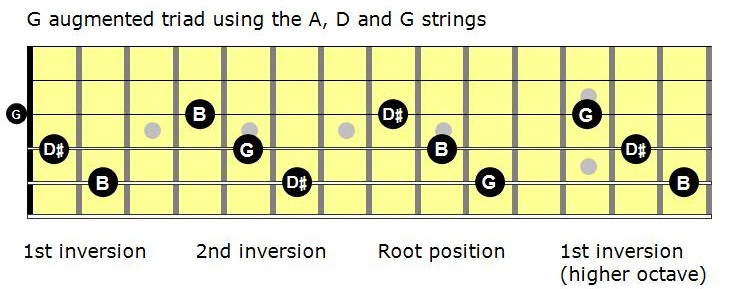
The Gflat augmented 2nd inversion contains 3 notes D, Gb, These note names are shown below on the treble clef followed by the bass clef The figured bass symbols for this chord inversion are 6/4 , so the chord is said to be in sixfour positionSecond inversion – interval 3, #5, 1;• The augmented triad is the same shape in all 3 inversions, but it is arrived at by changing a different note on each string • Go through the circle of 5ths starting with root position AThere are three halfsteps in between, so the major third is the note that is four halfsteps above the root An augmented triad is built by stacking two of these on top of each other For C major I would need




Basicmusictheory Com G Augmented Triad Chord




Basicmusictheory Com C Augmented Triad Chord
Play each augmented triad in root position, then 1st inversion, then 2nd inversion Play each chord up and down the keyboard for at least 2 octaves maybe 3 octaves Play them with your left hand, then play them with your right hand Then play them hands together Go through all 12 major chords, inverting every oneA chord's inversion describes the relationship of its lowest notes to the other notes in the chord For instance, a Cmajor triad contains the tones C, E and G;An augmented triad has a major third and an augmented fifth, so its fifth must be raised by a halfstep from a major triad Identifying Triads, Doubling, and Spacing Triads are identified according to their root, quality, and inversion;




Inversions Of Diminished And Augmented Triads Musical U



Mastering The Fretboard Augmented Triads Learn Jazz Standards
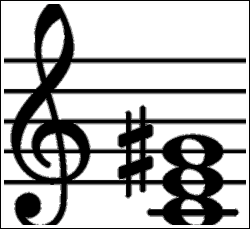
This step shows the G augmented 2nd inversion on the piano, treble clef and bass clef The G augmented 2nd inversion contains 3 notes D#, G, B These note names are shown below on the treble clef followed by the bass clef The figured bass symbols for this chord inversion are 6/4, so the chord is said to be in sixfour positionA Augmented triad 2nd Inversion E# (A) C# B Augmented Triad Root Position (B) D# Fx B Augmented Triad 1st Inversion D# Fx (B) B Augmented Triad 2nd Version Fx (B) D# Sets found in the same folder Music Theory > Chords > TriadsA chord is in first inversion if the third is in the bass If you take a C major chord and put the E in the bass, the result is a first inversion C major chord Second Inversion Chords A chord is in second inversion if the fifth is in the bass For example, putting G in the bass of a C major chord gives you a C major chord in second inversion



13 Triads Fundamentals Function And Form



Triads And Seventh Chords Open Music Theory
If you take a major triad and expand the fifth you will create an Augmented triad (a Major third with an Augmented fifth above the root) is used as an abbreviation for augmented A triad is in second inversion if the fifth is on the bottom (sometimes labeled 64



1




What Is An Inversion What Is The Difference With Root Position



Chapter 6 Classifying Chords With Strange Circles In Connectionist Representations Of Tonal Music On Au Press Digital Publications
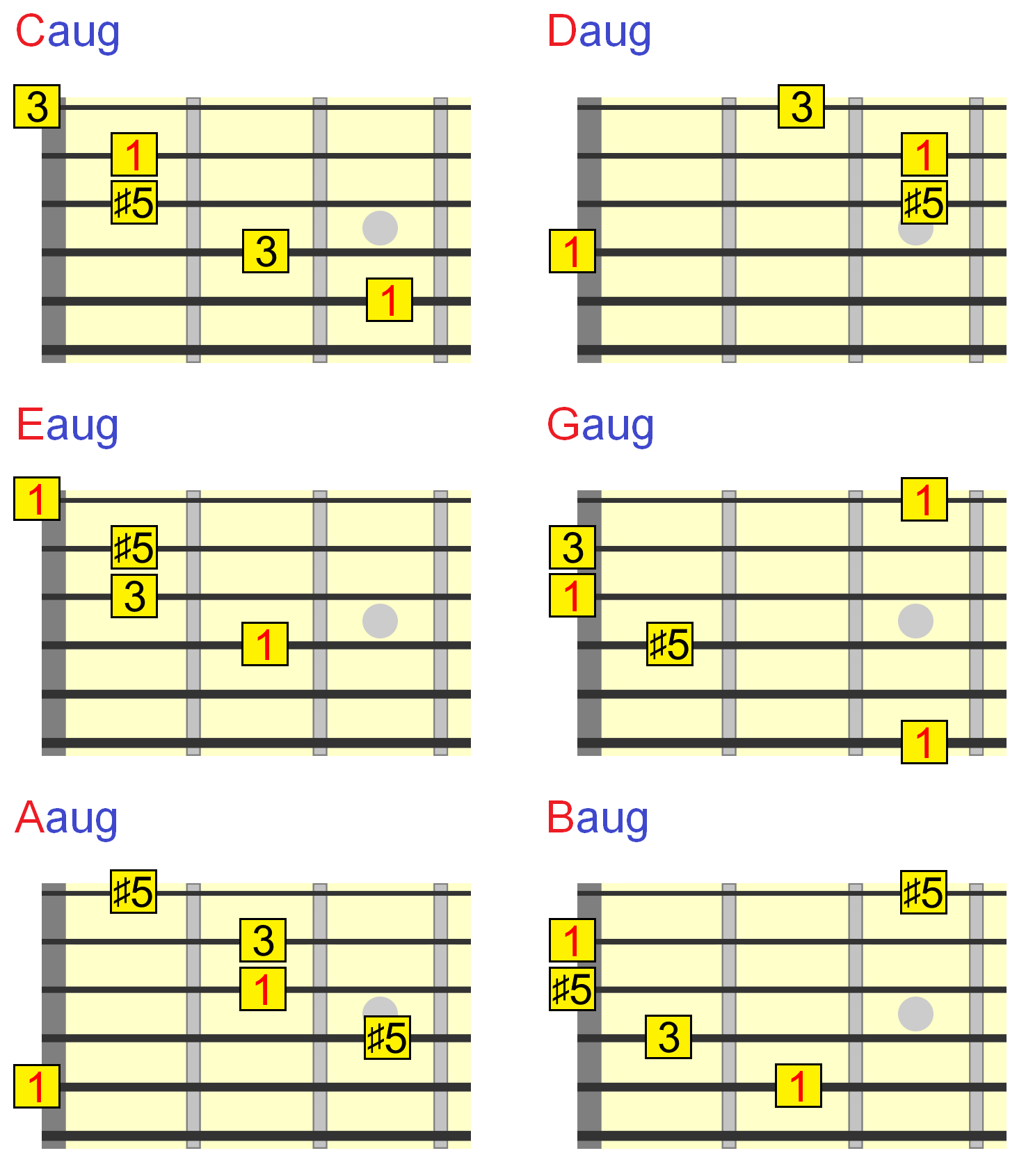



Augmented Guitar Chords Everything You Need To Know



Introduction
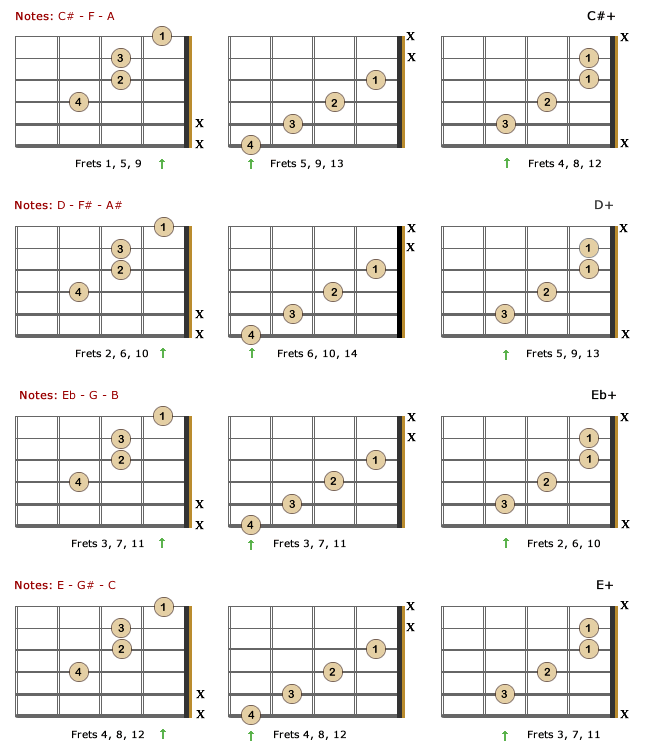



Augmented Chords For Guitar Theory Formulas Charts Bellandcomusic Com




Basicmusictheory Com G Sharp Augmented Triad Chord



Triads And Inversions



1
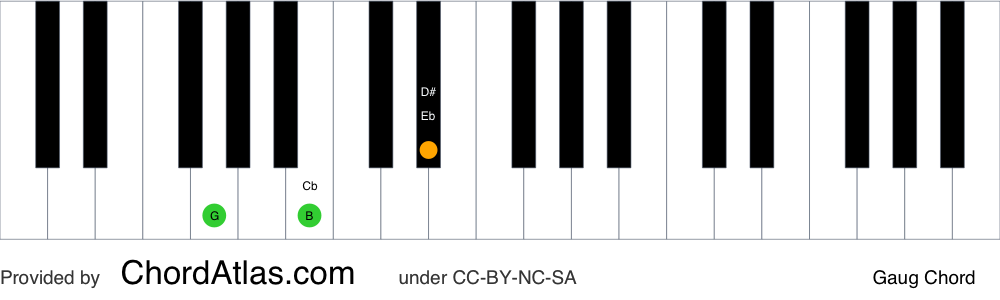



G Augmented Piano Chord Gaug Chordatlas
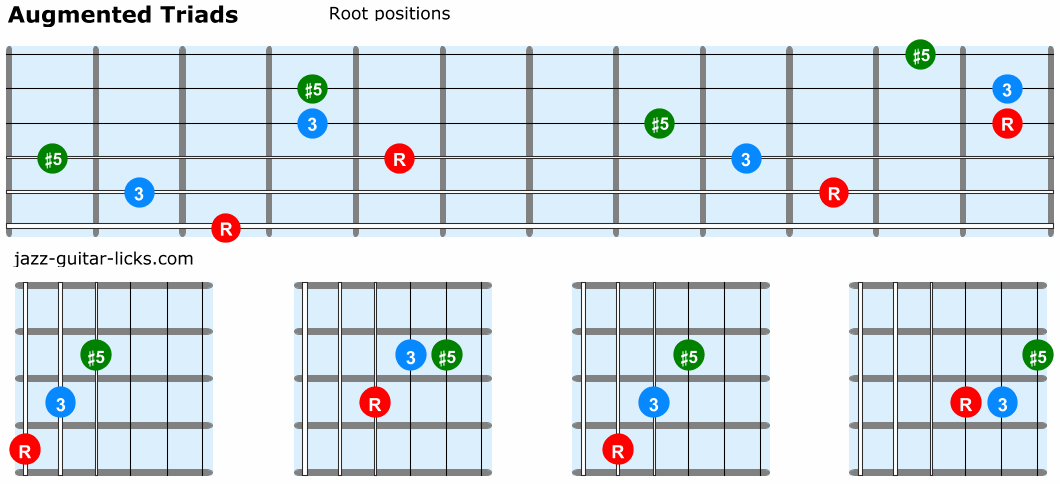



Triad Chords 84 Guitar Shapes Lesson With Pdf




Triad Jens Larsen




Augmented Guitar Chords Everything You Need To Know




Augmented Triad Wikiwand




Augmented Chord Music Elements Of Music
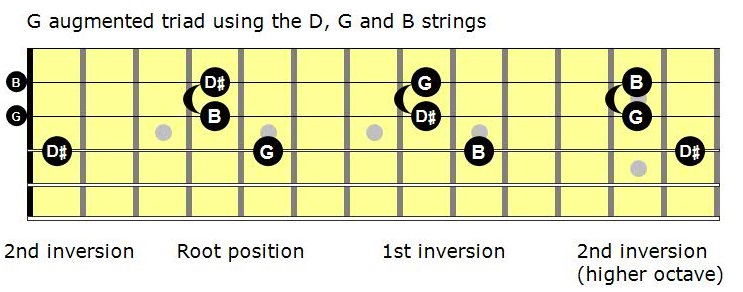



Mastering The Fretboard Augmented Triads Learn Jazz Standards
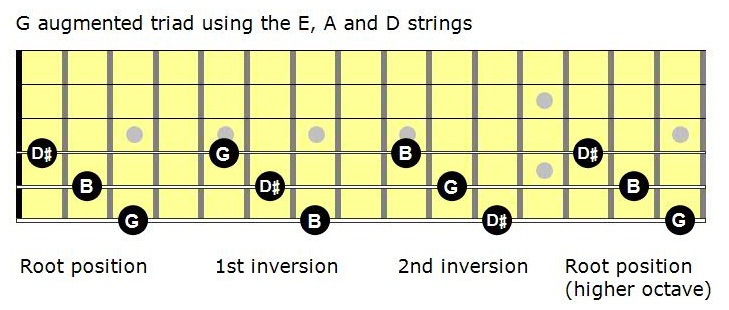



Mastering The Fretboard Augmented Triads Learn Jazz Standards



34 Other Chromatic Harmonies Fundamentals Function And Form



1
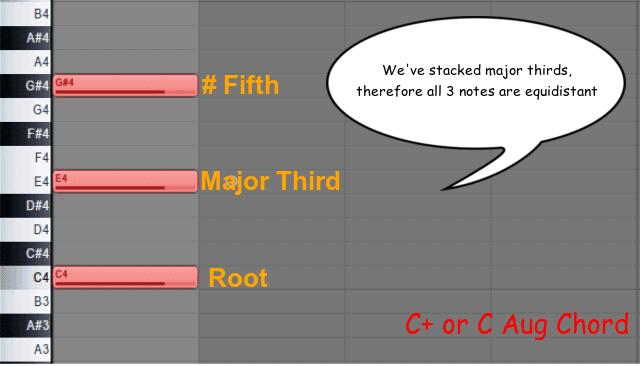



The Definitive Easy Guide To Augmented Chords W Examples



13 Triads Fundamentals Function And Form



The Augmented Chord Music Theory For Mandolin Simplymandolin




Triads Music Theory Academy




Basicmusictheory Com G Sharp Augmented Triad Chord




Basicmusictheory Com G Sharp Augmented Triad Chord




Basicmusictheory Com G Augmented Triad Chord
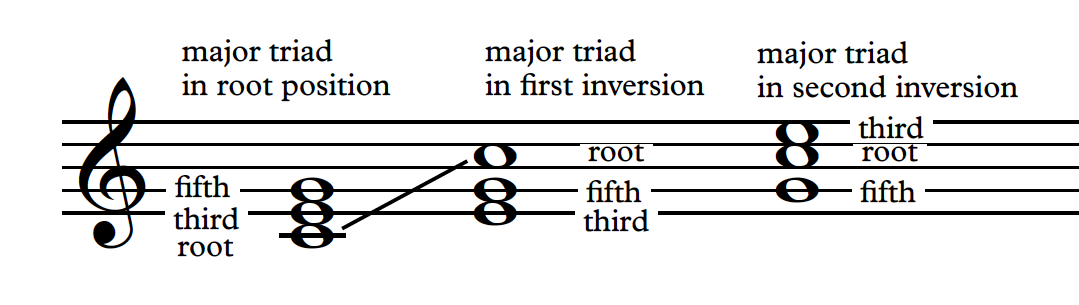



What Is An Inversion What Is The Difference With Root Position




Augmented Fifth Wikipedia
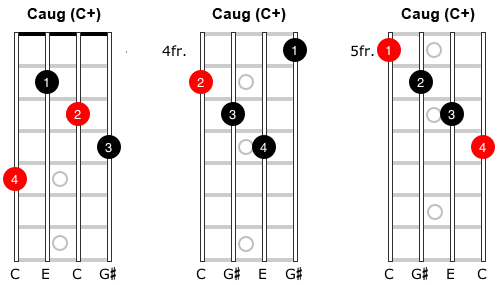



The Augmented Chord Music Theory For Mandolin Simplymandolin



Week 2 The Augmented Triad Cheat Sheet Hear And Play Music Learning Center
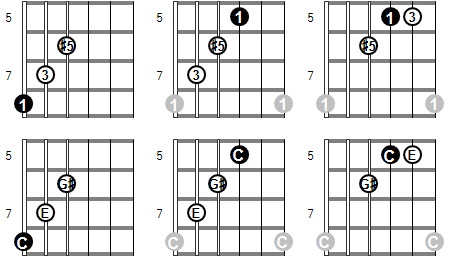



Augmented Triads The Nandi Method




Inverted Triads




Basicmusictheory Com G Sharp Augmented Triad Chord




Basicmusictheory Com A Augmented Triad Chord




Integrated Aural Skills Ear Training Triads In Review




Basicmusictheory Com G Major Triad Chord



Bandcoach Keys Scales Chords A Key Independent Approach To Chord Building




Augmented Sixth Chord Wikipedia



Lesson 12 Triads Part 1




Section 6 2 Basic Chord Concepts Offtonic Theory



Modern Music School



Bass Guitar Augmented Triads Second Inversion Sheet Music For Bass Solo Musescore Com



When We Learn Open Position Guitar



Introducing Triads Music Theory At Learnmusictheory Net




The Definitive Easy Guide To Augmented Chords W Examples



1




Master Triads Daniel Nistico




Harmony Its Theory And Practice At In Each Case The Chord Following The Dissonance Has Aroot A Fourth Above That Of The Dissonance Itself We Shall Findlater When We Have To



Mastering The Fretboard Augmented Triads Learn Jazz Standards




Capybara Guitar Posts Facebook




Basicmusictheory Com G Flat Augmented Triad Chord



Basicmusictheory Com D Augmented Triad Chord



Part 1 Of Triads Inside Out Learning Your Closed Voicing Triad Inversions Ry Naylor Guitar



Jazclass Jazz Theory 12 7th Chords 2



Triads And Seventh Chords Open Music Theory




Basicmusictheory Com G Flat Augmented Triad Chord



13 Triads Fundamentals Function And Form




Basicmusictheory Com G Augmented Triad Chord




Triad Tricks 4 Following On From Trick Ry Naylor Guitar




Theory Blog Music Theory Page 2




Understanding Inversions Music Practice Theory Stack Exchange




Section 6 3 Classical Chord Types Offtonic Theory



How To Play Triads On Guitar Jamieholroydguitar Com Jamie Holroyd Guitar




C5s1 Chords



Jazclass Jazz Theory 6 Triad Chords 2




Augmented Triad In Pathetique Sonata How Does It Function Music Practice Theory Stack Exchange




Triads And Pseudo Triads Of Music Arthur Fox Music



Mastering The Fretboard Augmented Triads Learn Jazz Standards




Basicmusictheory Com G Augmented Triad Chord



Unit 13 Music 110 Fundamentals Of Theory
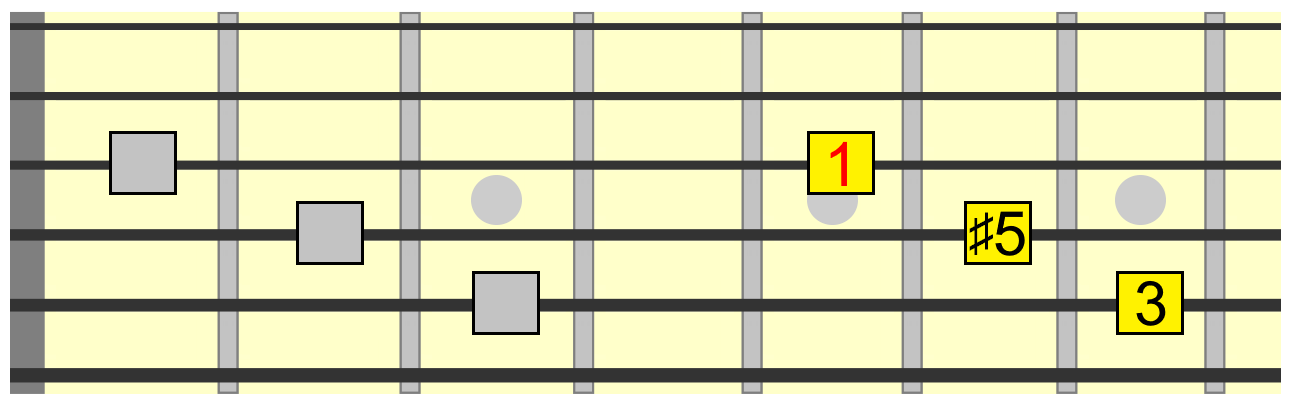



Augmented Guitar Chords Everything You Need To Know




Triads Music Theory Academy




Augmented Options Open Music Theory



The Jazz Sax Improvisation Blog Of Saxophonist Bobby Stern Bobbysternjazz Com




Basicmusictheory Com G Flat Augmented Triad Chord
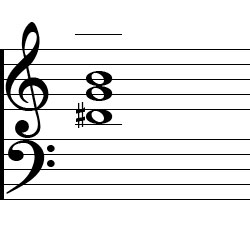



G Augmented Second Inversion Piano Chord




What Is A Chord Max Neil




Understanding Inversions Music Practice Theory Stack Exchange



Augmented And Diminished Chords Open Textbooks For Hong Kong




The Definitive Easy Guide To Augmented Chords W Examples



Triads



Triad Chords Inversions Triads Music Chord Symbols




Chord Inversion Music What Are They How Are They Used




5 2 Naming Triads


